
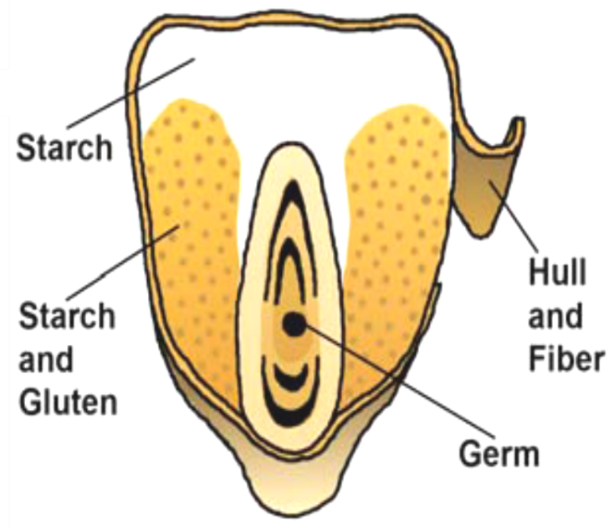
Corn is included in the cereal group. There are various materials in the structure of corn, which include starch, protein, fiber, oil, ash, moisture, and some minerals and vitamins. In general, a grain of corn consists of four main components, which are: starch, gluten (protein), fiber (along with the shell) and germ.
Corn seed can be consumed raw as an agricultural product and used in industry to produce products such as starch and sweeteners. In general, corn is used in the following cases.
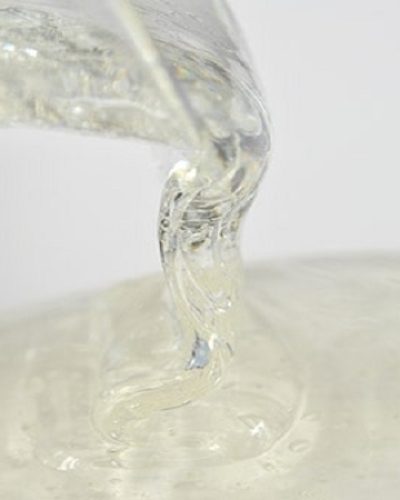

Glucose with the molecular formula C6H12O6 is a carbohydrate and is considered the most important sugar in the body’s metabolism. Glucose is in the form of white crystals and easily dissolves in water. Therefore, it is produced and supplied both in solid (powder) and liquid (thick syrup) form.
Due to its characteristics, glucose has found many uses, which are as follows.


Fructose is an isomer of glucose and its molecular formula is the same as glucose (C6H12O6). Fructose is known as fruit sugar and is found in honey, tree and ground fruits, apples, pears, berries, dates, flowers and vegetables. This substance may be present in plants both as a monosaccharide and as a combination with glucose.


Sorbitol, with the chemical formula C6H14O6 and the structure shown in Figure 1, is a sugar alcohol found in nature and metabolized more slowly in the human body than other common sugars. Sorbitol is the hydrogenation product of the aldehyde part of glucose, which adds a hydroxyl group to it. Sorbitol is a low-calorie sugar alcohol produced from dextrose. Chemically, it is a hexahydric alcohol and is also known as hexatol, D-sorbitol, D-glucitol. Sorbitol is naturally present in the sweet parts of many fruits such as strawberries, pears and apples, and was first extracted from the fruit in 1872.


Lactic acid with the formula CH3CH(OH)COOH is an organic acid with carboxyl and hydroxyl functional groups. Its molecular structure is shown in the figure below. Its chemical name is S-2-hydroxypropanoic acid. This acid is obtained from simple carbohydrates such as glucose, sucrose and lactose. It is produced naturally in the muscles as a result of intense physical activity.


Polylactic acid or polylactide is a biodegradable polymer that is produced from corn, cassava root, or sugarcane. Raw materials for the production of polylactic acid can be regenerated. Therefore, this polymer is also known as a bioplastic. Contrary to its name, this product is not a polyacid. Polylactic acid is a type of aliphatic polyester that is highly bioactive.


Glucose complex includes starch, glucose, fructose, sorbitol, lactic acid and polylactic acid production units. The purpose of setting up this complex is to produce downstream products of starch and glucose, i.e. fructose, sorbitol and polylactic acid from corn.
Unit 5, No. 7, Imam Khomeini St., Emad al-Islam St., Sahil St., Noor City, Royan City, Mazandaran Province
Unit 512, 5th floor, Palmyra commercial-administrative complex, Shahid Madani St., Narmak, Tehran, Tehran Province
Royan Petro Kimia Company (private shares) was established in 2013 with the registration date of 1663. . In the summer of 2014, this company became a member of the Association of Credit and Investment Banking Consultants and in 2022 succeeded in upgrading its rank to grade “B-3” in the fields of feasibility studies and investment opportunities in the petrochemical, refinery and chemical absorption industries.
Unit 5, No. 7, Imam Khomeini St., Emad al-Islam St., Sahil St., Noor City, Royan City, Mazandaran Province
Unit 512, 5th floor, Palmyra commercial-administrative complex, Shahid Madani St., Narmak, Tehran, Tehran Province
Royan Petro Kimia Company (private shares) was established in 2013 with the registration date of 1663. In the summer of 2014, this company became a member of the Association of Banking & Credit Investment Consultants and in 2022 succeeded in upgrading its rank to grade “B-3” in the fields of feasibility studies, introducing investment opportunities and financing in petrochemical, refinery and chemical industries.